PYL 105
PYL 105



Hooke's Law
Finding the spring constant
An object is elastic if
- it is deformed when a force is applied, and
- it returns to its origin shape when the force is removed
Our example of an elastic object will be a spring. You can apply a force
that stretches or compresses it. The force that opposes the applied force
is called the restoring force. If the restoring force is
proportional to the amount of deformation, the object is said to obey
Hooke's law.
One can study a spring from a force point of view or from an energy point of view.
We will look at a static spring from a force point of view and a moving (kinetic)
case from an energy point of view.
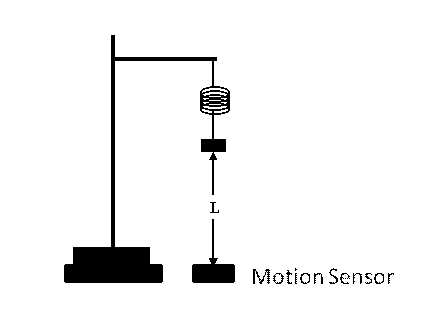
Static Case
Mass including hanger
( ) |
Distance L from sensor to hanger ( ) |
Displacement x
( ) |
Applied Force
( ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Calculate the "applied forces" (the weights, hanger included) and make a
plot of Applied Force versus L.
- Fit it to a straight line.
- What is the interpretation of the slope?
- What is the interpretation of the x intercept?
- What is the interpretation of the
y intercept?
(One of these intercepts is the equilibrium position -- the position from
which the spring's stretched distance is measured)
- Find the x's that correspond to your L's.
- The proportionality constant k is called the spring constant. What is the
spring constant for this spring? What are the units (dimensions) of the spring
constant?
- What is the meaning of the minus sign in Hooke's law?
|
Spring constant ( ) |
|
|
Equilibrium position ( ) |
|
Kinetic Case
- Pull one of the larger masses down a few centimeters and release.
- Record the motion.
- Build an Excel spreadsheet similar to the one for the Energy Analysis of
the Atwood Machine (previous lab). There should be a number of rows with each
row containing: position time, position, velocity time, velocity. Make the
adjustments (like last time) so that velocity and position are measured at
APPROXIMATELY the same time, calculate all kinetic energy terms, all potential
energy terms, total mechanical energy.
- Note that the gravitational potential energy (mgh) can be measured relative
to "any" reference point -- use the motion detector's postion, BUT the
spring's potential energy kx2/2 must be measured relative to its equilibrium
position k(x-xeq)2/2. (xeq was found above.)
- Make a plot of position versus time and velocity versus
time (2 items on one graph).
- Make a plot of total energy versus time and
gravitational potential energy versus time (2 items on one
graph)
- The total energy should be a flat line (your graph probably has a small oscillation).
One thing that was ignored was the mass of spring. Since the spring
has mass it has kinetic energy! Also, since the spring has mass that mass is
contributing to the stretching the spring as well as the potential energy. Because
the spring is not a point object not all of its mass is moving at the same
rate (e.g. the top part moves less than the bottom part). Theory predicts that
this distribution of mass is equivalent to 1/3 of the spring's mass for kinetic
energy but 1/2 of the springs mass for gravitational potential energy and 1/2 for finding
the spring equilibrium position.
Mass including hanger including half of mass of spring
( ) |
Distance L from sensor to hanger ( ) |
Displacement x
( ) |
Applied Force
( ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Find the spring parameters if the spring's mass (half of it) is accounted for.
|
Spring constant ( ) |
|
|
Equilibrium position ( ) |
|
- Copy your data to a new sheet. Add one half of the mass of
the spring to your masses and redetermine the equilibrium position. Add one half of the
spring's mass to your gravitational potential energy and 1/3 of the spring's mass to
your kinetic energy. Is the resultant total energy any flatter?


 PYL 105
PYL 105





 PYL 105
PYL 105